What is Tailgating?
Cyber threats have become increasingly sophisticated, yet physical security is often overlooked. Among the various potential threats, tailgating is a serious concern. This attack occurs when an unauthorized person sneaks into a restricted area by following closely behind an authorized individual.

An attacker might also gain access to your IT systems by acquiring stolen credentials, allowing them to breach business networks and sensitive information. This form of tailgating can have serious cybersecurity implications.
There are several variations of tailgating attacks. Are you prepared to examine these threats in more detail and uncover the risks they pose to your organization?
What is Tailgating Attack?
Table of Contents
A tailgating attack is a physical security breach where an unauthorized person gains access to a restricted area. This happens when the attacker follows closely behind someone with legitimate entry, such as an office employee. This sneaky method allows the attacker to bypass security measures undetected.
While high-profile threats like ransomware and phishing often receive more attention, tailgating and piggybacking are frequently overlooked. As a form of social engineering, tailgating poses significant and unmeasurable risks to modern enterprises, making it a serious concern for businesses.
- Cyber-criminals take access to the restricted area
- Follow the prohibited authentication process
- Manipulation of an authorized employee
Attackers employ different authenticated sources such as a biometric scanner, or passcode-protected door for secure entry. It is important to understand the difference between tailgating and piggybacking for effective cyber attack detection in most situations.
Differentiate Tailgating vs Piggybacking
It looks strange to many that tailgating and piggybacking attacks are often used interchangeably. The noteworthy thing is that the two come with differences as well. Tailgating attacks occur when an attacker follows an uninformed user to gain unauthorized access to an area. The attacker misuses the trust of the authorized individual to gain access.
In contrast, piggybacking attacks occur when an employee or ex-employee deliberately provides illegal individual access to a secure environment as an integral part of a coordinated attack. It is executed against the company’s policy.
When it comes to distinguishing tailgating from piggybacking, it clarifies their vulnerable sources. Whether the roots stem from neglectful actions (tailgating) or unmonitored helpfulness (piggybacking), each requires custom preventative strategies within cybersecurity frameworks to control digital risks.
Examples of Tailgating Attack (How Does it Work?)
Tailgating is most commonly used by attackers to misuse physical IT equipment or gain access to sabotage the endpoints hooked to the company’s networks. Businesses with inadequate security measures are at higher risk of such breaches.
Implementing robust IT consulting solutions can help organizations strengthen their security posture by enhancing access control, employee awareness, and visitor management systems. Do you want to deceive tailgate attackers? Let’s understand the following methods followed by malicious actors to get illegal access to the protected area.
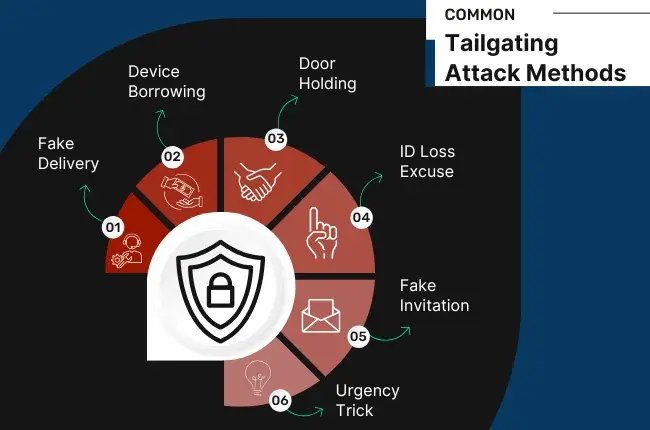
1. Poses as a Delivery Person
In the age where the e-marketplaces trend is rampant, an intruder may pretend to be a delivery man or vendor to get smooth access to your premises. They dress up well to prevent suspicion and receptionists can easily allow them to deliver the parcel, supplies or other items for someone on a specific floor or room. This is how an attacker reaches closer to the target for attack.
2. Borrows the Device
In some cases, an intruder may ask to use an employee’s official device for any wrong reason. For example, they craft the reason that their battery is dead. The attacker then installs dangerous software or copies the victim’s sensitive information such as credentials or financial data.
3. Asking to Hold the Door
An attacker may pose to be a fellow worker and ask someone to hold the door entering the business premises. To leave a trusted impression, the attacker can hang out in easily accessible premises, or even engage in talks with real on-site workers. In this kind of malicious act, tailgating also involves social engineering because the victim is unknowingly being manipulated.
4. Complaining ID Loss
Another smooth way opted by a social engineer to gain entry to the targeted area is to pretend to be a staff member who has missed to bring the ID card. They use a highly convincing tone and the employee is befooled by handing them an entrance pass or helping them inside.
5. Acting as Invited
Sophisticated social engineers try to test the waters first. They present themselves as a guest to someone in the office. Before making this move, they have likely already researched data including the company’s name, and the names of the top brass employees to make their plan more believable.
Forbes Survey revealed 2023 data breach incident cost $4.76 million to IBM due to social engineering. The emerging technologies are making all the above-shared methods more convincing for AI cybersecurity risks.
What Enterprises Are Prone to Tailgating Incidents?
Many enterprises focus on other security protocols but often fail to prepare for tailgating attacks. This happens because organizations tend to underestimate the likelihood of cyber attackers executing “boots on the ground” style intrusions.
However, any enterprise with sensitive data is at risk of tailgating attacks. Despite the proximity of this threat, implementing proper visitor management systems and identity verification at all entry points can significantly reduce the chances of such breaches.
- Business premises with multiple entry points – If your organization has multiple entry points, you’re going to be an easier target for cyber attackers to execute their plan.
- Companies with higher staff turnover – Displeased ex-staffers can gather sensitive data on your internal security strategies, and the ill actors may use this information for nefarious gains.
- Organizations with multiple meeting rooms – Offices with several meeting rooms and disparate IT resources create an appealing platform for malicious actors to access unauthorized cyber resources without being traced.
According to a Feb 2024 incident, journalist Charlotte Cowles revealed she lost $50,000 after a dreadful social engineering scam. It illustrates a social engineering attempt that more likely leads to sensitive data and financial losses.
Serious Effects of Tailgating
Tailgating is a serious criminal offense that allows unauthorized individuals to access valuable assets and sensitive information, sometimes with the unintentional assistance of victims. The consequences of such breaches can be severe and far-reaching.
According to a Forbes about social engineering report, 27 cloud customers of a software development company, Retool, lost access to their accounts after an attacker manipulated IT team members into clicking a link to address a payroll-related issue. This incident, a result of social engineering, highlights the grave consequences of tailgating attacks. At Advanced IT, we ensure your employees are trained to recognize and respond to such deceptive tactics, reducing the risk of security breaches caused by human error.
Let’s explore the key effects discussed below:
| Compromising of Vulnerable Information | It can compromise highly sensitive data and information, posing a severe threat to business confidentiality. |
| Monetary Loss | Tailgating ends up in sensitive data theft and reputation damage. It can cause significant financial loss to an organization. |
| Operational Disruption | Hackers gaining access through tailgating attacks can naturally disrupt operational activities, leading to loss of business and delays in service. |
| Reputational Brunt | Consistent security breach incidents significantly rupture a company’s market reputation. It highly impacts dealings with clients, stakeholders, and partners. Undoubtedly, this can have grave implications for your business’s growth. |
| Security Infringement | Tailgating enables all unauthorized individuals to gain physical access to highly protected areas, compromising the overall security posture of a business facility. |
How to Prevent Organizations from Tailgating Attacks?
Vade researchers findings revealed that the number of social engineering attacks rose by 173% during the second quarter of 2023. Given the risk prevalence, luckily, there are several preventive measures against tailgating. Where the firewall or endpoint security software stops helping you against tailgating attacks, these preventive steps can guide you to upgrade the security posture within your company.
1. MFA Security Method
Multi-factor authentication is an effective security technique to prevent tailgating and enhance security levels. Users are required to provide multi-tier identification, such as biometrics, passwords, face recognition or security tokens. This makes it challenging for unallowed individuals to gain secure access. MFA effectively controls data breach incidents.
2. Smart Security Badges
Advanced security methods provide smart badges. They are physical credentials mainly equipped with embedded tech, like RFID small chips, or microprocessors. It is challenging to replicate them, making this technique a better protection than manual ID-card-based authentication.
3. Install Surveillance Cameras
Surveillance cameras make it easier to check any unauthorized access activity in real time. It helps security to respond promptly in case of any suspicious attempt. Above a deterrent, it also provides visual documents as solid evidence in detecting actual offenders in case of tailgating attempts.
4. Security Awareness Training Program
It is mandatory to provide spillage cyber awareness to employees. It enables them to understand social engineering tricks to help mitigate tailgating attacks. Provide security awareness training programs supported by simulating attacks. It provides them with better exposure to deal with any related situation in real time.
5. Use Electronic Keycard
This electronic mechanism is a security token or credential that grants you smooth access. This method requires a keycard reader. It is typically installed on the required door to work. It allows you to gain access by either swiping the card, tapping it on the reader, or inserting it. With secure access, it is easy to control tailgating incidents.
6. Implement Two-Person Rule
Apply two-person control mechanisms effectively designed to achieve top-tier security for sensitive business operations or material. This rule dictates access and actions require the presence of two or more authorized individuals for continuous monitoring and intervention if any unwanted situation occurs.
7. Turnstile Access Control System
It is an effective type of access control system. Turnstiles permit only one individual to pass at a time. It can easily be configured to enforce one-way human traffic to restrict unauthorized access to sensitive facilities. By monitoring the flow of people entering the facility, tailgating can be reduced to a significant extent.
8. Install Mantrap Doors
It is another form of access control system consisting of a limited space and two interlocking doors. It ensures one set of safety doors must be tightly closed before the other door can be opened to pass through. Mantrap doors significantly reduce unauthorized access and tailgating attempts.
9. Physical Security Guard
Meeting rooms or reception areas protected by physical security officers add a strong security layer. It effectively ensures authorized access to the sensitive areas of the business facility in result mitigating tailgating incidents.
Tailgating Attack FAQs:
What is an Example of IT Tailgating?
Tailgating is possible to appear in both physical and virtual settings with the common purpose of accessing confidential data. In IT tailgating, intruders send malicious emails that appear to be from valid sources to request sensitive data or information.
What Type of Attack is Tailgate?
It is a physical security threat in which an intruder or hacker gains access to a sensitive area for nefarious purposes. This is possible by following someone with legal access to the facility, such as a staff member.
What Does Tailgating Mean Hackers?
Tailgating refers to an unauthorized individual following an authorized person through a safe entry point without informing the authorized person.
Tailgating is no less harmful than phishing scams or ransomware attacks. By implementing hybrid cloud best practices, user awareness programs and secure access points, it is easy to protect both physical and IT settings.
Facing IT Challenges in Chicago?
Schedule a consultation with our expert team to get the help you need!

